Structure of Neuron in Human Brain
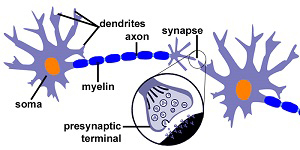

Structure of Neuron in Human Brain

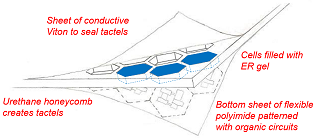
An Example of Structured Computational Polymers

Structured Computational Polymers
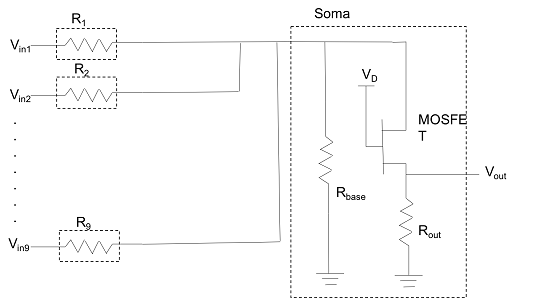
Structured Computational Polymers (SCPs) are intelligent meta-materials that combine sensing, cognition, and actuation into bulk materials, bridging the gap between novel material characteristics and integrated design paradigms. The research on Softskin Robot in Collaborative Robotics Lab with Dr. Voyles has developed a neuromorphic architecture that aims to mimic information processing the way biological systems do. A hardware implementation of an artificial neural network (ANN) was completed. The metal-oxide semiconductor and silicon-based memristors (memory resistors) were utilized as a synapses for synaptic functions such as spike and timing dependent plasticity. In the design, memristors are arranged into a cross-bar with pre- and post-synaptic neurons being locate on adjacent sides of the cross-bar.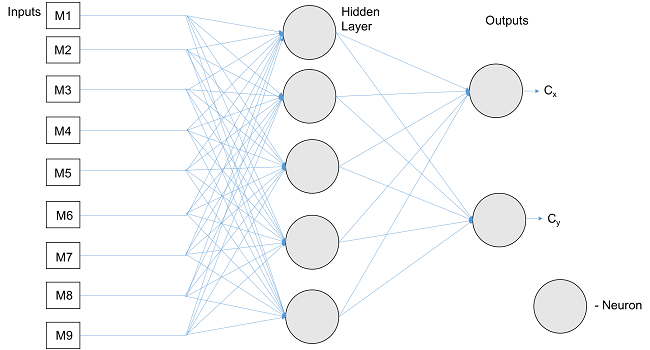
Synthetic Neural Network architecture with three distinct layers 9 inputs, 5 neurons in hidden layer and 2 outputs
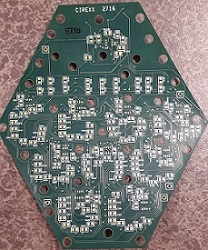
Hexagonal cells of SCP developed in a flexible PCB
Past Works on Softskin Robot
[1] R.A. Nawrocki, X. Yang, S.E. Shaheen, R.M. Voyles, "Structured computational polymers for a soft robot: actuation and cognition," in IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, April 2011, pp. 5115-5122.
[2] R.A. Nawrocki, R.M. Voyles, S.E. Shaheen, "Neurons in Polymer: Hardware Neural Units Based on Polymer Memristive Devices and Polymer Transistors," in IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, v. 61, n. 10, 2014, pp. 3513 - 3519.
Implementation for Prototype
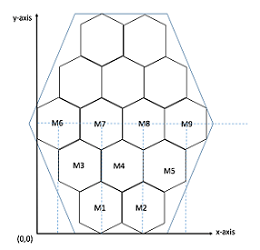
I had been assisting Praveen Abbaraju, PhD student in CRL to develop a prototype of SCP. The hexagonal cells were designed on a flexible PCB. The synthetic neural network of 9 inputs, 5 hidden layer neurons and 2 outputs was implemented in this PCB design and currently on a testing phase to reduce the error percentage of output results. We are expecting to get a different output value in voltages based on the location of hexagonal cells. M1 through M9 have different x- and y-coordinates and when the voltage was applied to the cell, the output should indicate the difference in location of the hexagonal cells.